The hip joint is the largest joint in the human body. Every day he makes thousands of movements walking, running, climbing stairs and doing physical exercises. Constant loads, inflammatory processes, injuries and diseases can cause coxalgia, pain in the hip joint. It is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence as early as possible to avoid mobility limitations and disability.
Classification of painful sensations
During a visit to the doctor, it is necessary to describe in detail the nature of the pain: its degree of severity, intensity, frequency - the accuracy of the diagnosis depends on this. Depending on the nature of the pain, it can be:
- Spicy.In this case the pain is intense, even unbearable. It can appear suddenly and also disappear suddenly. As a rule, a patient with acute pain can accurately indicate the area of its localization. Acute pain can radiate, spreading to areas closest to the source of the pathology.
- In pain.The pain is not that intense, it can sometimes feel like discomfort and does not have an exact location. Aching pain may intensify during movement or after exercise and disappear for a while.
- Chronic.This category usually includes pain that occurs with varying regularity for more than six months. Chronic pain is generally the most difficult to treat.
Possible sources of pain
The main causes of pain in the hip joint are:
- injuries,
- infectious diseases,
- inflammatory processes,
- degenerative changes in the tissues,
- pathologies of the development of the musculoskeletal system.
Injuries
With traumatic damage to the hip joint and femur, pain occurs immediately, accompanied by redness and swelling of the tissue, limited mobility of the limb and the formation of extensive hematomas. Depending on the severity of the injury, the pain can be more or less intense.
If you hit or fall on your side, soft tissue bruising may occur. It is characterized by the formation of hematomas, pain at the site of the lesion intensifies upon palpation. Unlike dislocation and fracture, with a bruise there is no limitation in the mobility of the injured leg, there are no visually distinguishable deformities, and the limb completely retains its functions.
Dislocation of the hip joint in a healthy person can occur only in the event of a very strong physical impact, for example, in the event of a fall from a great height or in a traffic accident.
The limb takes a position of forced rotation, most often inward, less often outward. The pain is intense, accompanied by swelling, numbness (if the nerves are affected), the victim cannot move the injured limb.
Fracture of the femoral neck
The cause of pain in the hip joint can be a violation of the integrity of the femoral neck, an injury that mainly affects older women who have crossed the threshold of 60 years. Age-related and hormonal changes in the body after menopause accelerate the calcium leaching process, making bones brittle and brittle even with minor exposure. A fall, a bruise or even a careless movement can lead to a fracture of the femur at its thinnest point, where the shaft connects to the head embedded in the hip joint.
Symptoms of a hip fracture are:
- pain in the pelvic area, radiating to the groin and lower back, aggravated by tapping the heel;
- shortening of the injured leg;
- limited mobility, inability to lean on the injured leg;
- outward rotational position of the limb;
- "Locked heel" syndrome – the inability to lift the straight leg off the surface from a lying position.
A fracture of the femoral neck can be affected: in this case the bone fragments fit into each other. In this case, the functions of the limb can be partially or even completely preserved, but when the fragments are crushed, signs of injury will appear in full. Such an injury requires immediate intervention, so if you suspect a fracture, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Inflammatory processes
One of the main causes of coxalgia is inflammatory processes in the tissues of the joint or its surroundings.
Arthritis is inflammation of the cartilage tissue in the joint. The causes can be infections, chronic injuries, metabolic disorders, excessive stress, systemic connective tissue diseases. Symptoms of the disease, in addition to pain, which intensifies after exercise or at night, are redness and swelling of the tissues in the area of the affected joint, local increase in temperature and limited mobility of the leg.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic connective tissue disease of an autoimmune nature. Women are more susceptible to the disease. It affects both small and large joints, most often paired ones. Characteristic symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis:
- joint pain, which worsens at night and disappears after movement;
- formation of subcutaneous compactions in the area of the affected joint, the so-called rheumatic nodules;
- redness, swelling and local increase in temperature in the affected joints.
Bursitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the synovial bursa of a joint, accompanied by a pathological accumulation of exudative fluid in the tissues of the joint. The main causes of the development of the disease are considered injuries, excessive physical activity, infections and complications of arthritis of various etiologies. The pain caused by bursitis occurs deep inside and spreads to the outer surface.
Ankylosing spondylitis is an idiopathic disease, that is, in most cases it is not possible to establish the exact causes of its onset. It is assumed that the pathology is genetically determined and that hereditary predisposition plays an important role in its development.
Most often, the manifestation of the disease occurs at the age of 20-30 years, its first symptoms are pain in the lower back, hips and buttocks, worsening at night, stiffness, rapidly developing ankylosis - immobility of the joints. In the later stages, if untreated, the disease causes serious deformations of the joint tissue, leading to profound disability.
Degenerative tissue changes
Coxarthrosis or osteoarthritis of the hip joints, a degenerative change in the cartilaginous tissue, is a common cause of coxalgia in people over the age of 40-45. The disease is chronic and constantly progressive. The causes of its development are considered chronic injuries, hereditary predisposition, age-related changes and concomitant inflammatory diseases of the joints. In young people, the development of coxarthrosis may be due to congenital dysplasia of the hip joint.
Symptoms of pathology:
- pain in the groin, lower back, buttocks, thigh, which increases with movement and decreases at rest;
- muscle weakness;
- intermittent claudication, duck-like gait with bilateral joint damage;
- limb dysfunction, difficulty in abduction, adduction, rotation.
Infectious diseases
Infectious arthritis, which is also a common cause of coxalgia, can develop due to the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the joint tissue from a distant focus of a viral or bacterial infection through the bloodstream. It can be caused by streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and tuberculosis bacilli, spirochetes pallidum, influenza viruses and other agents.
In infectious arthritis, joint pain is accompanied by redness and swelling of the surrounding tissues, as well as general symptoms: fever, malaise and weakness.
Other reasons
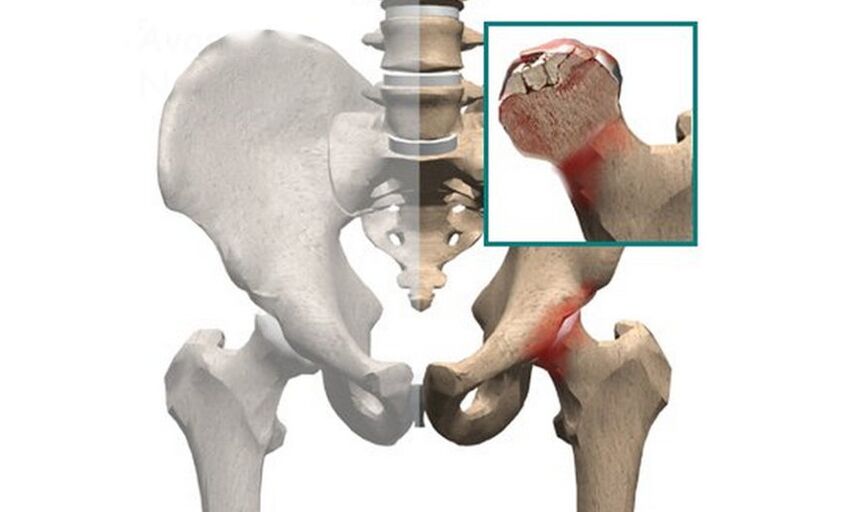
In addition to injury, inflammation, and infection, hip joint pain can be caused by:
- Innervation disorders.Inflammation and pinching of nerve roots, particularly the sciatic nerve, can cause pain in the hip, inguinal triangle, and buttocks.
- Formation of neoplasms, including malignant ones, in the tissues of the joint and its surroundings.
- Aseptic necrosis of the femoral head.Chronic poor circulation in the tissues causes degenerative changes in the cartilage and bone tissue and can lead to the total destruction of bone structures.
- Juvenile epiphysiolysis.Chronic pain in the hip joint in children and adolescents can be caused by the development of epiphysiolysis - a pathological displacement of the femoral head caused by hormonal disorders in the body. Boys are more susceptible to the disease, but in rare cases it is also diagnosed in girls. As a rule, the pathology is accompanied by delays in sexual development and endocrine disorders.
Hip joint pain is a common occurrence in women in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. Causes of coxalgia in pregnant women:
- an increase in body weight and a shift in the center of gravity, redistribution of the load on the musculoskeletal system;
- natural hormonal changes: shortly before giving birth, a woman's body begins to produce a hormone that relaxes the ligaments;
- pressure of the enlarged uterus on large vessels and nerves, disruption of innervation and blood circulation in the pelvic organs and lower extremities;
- calcium deficiency in the body of the expectant mother.
If the pain during pregnancy was caused by the above factors, then within a few weeks of birth they should disappear without a trace. If, a month after the birth of the baby, the pain is still present, you should consult a doctor.
Alarming symptoms
Pain in the hip joint is an alarming symptom, which is a mandatory reason for a visit to the doctor. The earlier the cause of coxalgia is identified, the greater the chance of a complete recovery. However, there are cases where seeking medical help should be immediate:
- pain in the joint area occurs after a fall, blow, bruise or any other injury, while the mobility of the limb is impaired;
- the tissues around the joint are red and swollen and the general body temperature rises to feverish levels (38 and above);
- there are problems with defecation and urination.
Diagnostics
The first step in determining the cause of hip pain is to see a doctor. The surgeon or orthopedist will take the anamnesis, find out the nature of the pain, the frequency and degree of its manifestation, and also examine the patient to evaluate the mobility of the joint and the condition of the surrounding tissues. To make an accurate diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods can be prescribed:
- general, biochemical, serological, immunological blood tests;
- x-ray of the pelvic bones, thighs, hip joints;
- ultrasound examination of the tissues of the joint and the tissues surrounding it;
- MRI and computed tomography to obtain an accurate three-dimensional image of the affected area;
- endoscopy of the joint using a probe inserted into its cavity;
- puncture to study effusion - accumulation of pathological fluid in the joint capsules;
- tissue biopsy.
Treatment methods
Treatments for conditions that cause hip pain depend on the underlying cause. In cases where the pain was caused by an injury, the main method of conservative treatment will be joint immobilization; in some cases surgery may be necessary. If the pain is inflammatory in nature, non-steroidal or hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs can be prescribed; For general infectious diseases, antibiotic therapy or antiviral drugs will be necessary.
Pain syndrome, regardless of the cause of its occurrence, is relieved by taking analgesics or blocking injections.
Immobilization
Immobilization is often prescribed for joint injuries. Tight bandages, plaster splints or plastic orthoses can be used for fixation.
Pharmacological therapy
Depending on the cause of coxalgia, the following may be prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or glucocorticoids to relieve inflammatory processes;
- chondroprotectors to slow degenerative changes in joint tissues;
- antibiotics and antiviral drugs in case of arthritis of an infectious nature;
- muscle relaxants to reduce muscle spasms.
Physiotherapy procedures
In the rehabilitation phase after injuries, as well as during the period of remission of diseases, the following physiotherapeutic methods are used to restore joint mobility, improve blood circulation and restore the function of the limbs:
- Physiotherapy,
- massage,
- magnetotherapy,
- balneotherapy,
- laser therapy,
- UHF heating,
- hirudotherapy.
Endoprosthesis
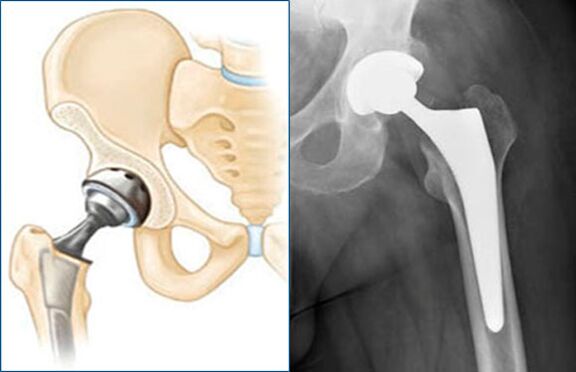
In some cases, conservative treatment of hip joint pain may be ineffective. Aseptic necrosis, advanced stage coxarthrosis, fracture of the femoral neck in the elderly are direct indications for endoprosthetic surgery - replacement of the head and acetabulum of the hip joint with a prosthesis made of chemically and biologically inert materials.
The operation allows you to shorten the rehabilitation process and return the patient to full movement.
Prevention of coxalgia
A number of preventive measures will help prevent the onset of pain in the hip joints, including:
- regular physical activity to strengthen muscles and ligaments;
- nutritious and balanced diet;
- body weight control, since overweight and obesity create additional stress on the musculoskeletal system;
- avoid injuries and excessive physical activity;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely and adequate treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases;
- regular preventive examinations with a doctor.























