The osteochondrosis of the cervical column is a chronic lesion, slowly progressive of the vertebrae of the cervical column (from the first to the seventh), which begins with the destruction of the intervertebral discs and ends their subsidia).
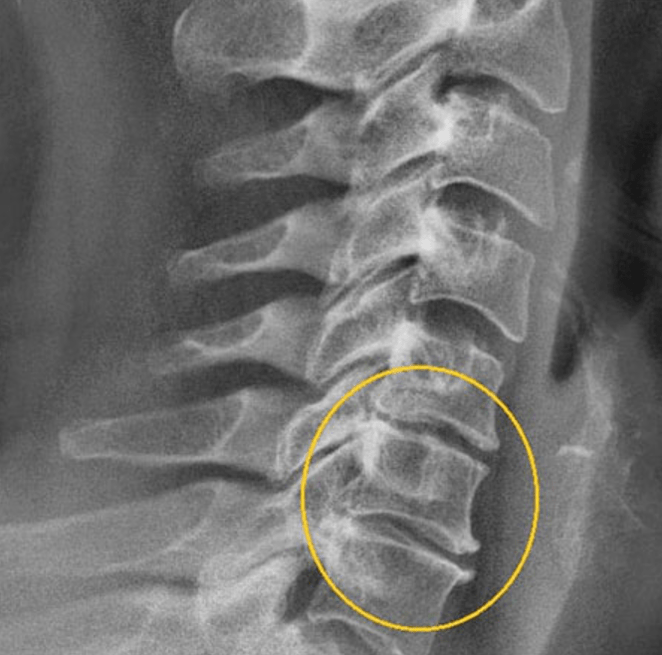
Subsequently, neurological (compression, inflammation of the nerves and their consequences) and vascular complications (compression of the vertebral artery and the consequences of blood circulation disorders) are combined with the clinical symptoms of osteochondrosis. With cervical osteochondrosis, they are headache, dizziness, orientation loss, nausea, sharp drops of pressure that are difficult to normalize. Osteocondrosis is a common pathology, whose symptoms at the age of 45 appear in 90 % of people (regardless of the genre), before the others - for employees who lead a sedentary lifestyle. The lesion of the cervical region is diagnosed as often as lumbar osteochondrosis. This is due to the excessive mobility of the neck and the weakness of the muscles surrounding the spine in this area.
The essence of the pathology that happens with it
The intervertebral disc (abbreviated MPD) is a nucleus of the aqueous pulp in the center and the elastic and stronger fibrous shell that surrounds it. The bodies of the nearby vertebrae are adjacent to it and below. The receipt (and excretion) of substances and water in the intervertebral disc occurs due to the diffusion (direct and inverse filtration, the penetration of molecules on the disc and back) from the bone tissue of the vertebrae. The gradual aging of the tissues of the intervertebral disc leads to the fact that the reception of the necessary substances slows down and under the influence of provocative factors (pressure, load), completely ceases. The dense tissue of the fibrous membrane is covered with cracks, loses its elasticity, the nucleus of the pulp at the center came out (it loses water). This leads to the fact that cervical osteochondosis progresses:
- MPD loses height;
- The bodies of the vertebrae are moved, the nerve roots are crushed and begin to grow with bone peaks, trying to evenly distribute the growing pressure (spondylosis).
Over time, the ligaments are involved in the ossification process, they are impregnated with calcium in the place of attachment to the vertebrae and become the cause of rigidity, bond of the neck. Since people continue to load the spine: they are actively moving, they sit in an uncomfortable position:
- The bodies of the nearby vertebrae are increasingly compressed by the APD;
- This leads to the fact that the octopus core (rather what remains) is pushed forward or backwards (more often towards the front longitudinal ligament, since it is rather thin in the cervical region).
This protrusion is called the protrusion (the shell of the disc has not yet exploded, but has only changed shape), it presses on adjacent tissues, which leads to the occurrence of muscle tension, pain and other pronounced symptoms with which the cervical osteochondosis proceeds. Over time, the fibrous shell of the disc is still torn and part of the Pulpic nucleus is crushed in the fabric (this turning point is called hernia). At this stage (it is 4 phases), all the acute symptoms of the disease can appease (a small part of the nucleus is absorbed or covered with calcium and ceases to irritate the surrounding tissues) or, on the contrary, they will lead to the development of the ischemic stroke of the brain (deficiency of oxygen, death of a hunger area) and disabilities.
Causes provocative factors
Considering the causes of osteochondrosis, it is worth noting that the basis of violations is the natural aging of the tissues of the intervertebral disc. The process can accelerate several provocative factors:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Congenital defects in the development of the cervical column (deformation of the body of the first cervical vertebra).
- Damage and surgical interventions.
- Excessive mobility of the cervical region (for example, in sports training).
- Lack of physical activity (sedentary work).
- Violation of posture (curve).
- Age.
- Nervous stress.
- Hypothermia.
Four phases (grade) and symptoms
With osteochondrosis in the cervical column, all manifestations intensify from stadium to the other, the more changes occur on the intervertebral disc - the stronger the symptoms of cervical osteochondosis. In the initial phase of a person, muscle tension in the neck and shoulders can be disturbed, due to which they tire quickly. So the main sign of the pathology appears: the pain it gives to the back of the head, shoulders, arms, chest, can be masked as pain in the teeth. A person begins in dizziness, the concentration of attention weakens, vision and hearing, this worsens the quality of life and does not affect its ability to work well. Gradually, the symptoms increase and intensify: a person wakes up with a feeling of rigidity in the spine, during the periods of exacerbations any acute movement (for example, sneezing or a heel on the floor) causes a cutting pain in the neck and along the affected nerves, it becomes difficult to raise the hand or keep the object in the fingers. At night, the heartbeat can intensify or the appearance of a feeling of lack of air can be worried: the patient cannot breathe deeply, due to pain, a person is unable to move, turn the neck or raise his hand. In symptoms, osteochondrosis in men is almost no different from osteochondrosis in women (they are most often worried about headaches.
1st stadium (degree)
The intervertebral disc lost its elasticity and fell.
At this stage, with osteochondosis of the cervical region, tension, fatigue, muscle fatigue and neck pain appears.
The first symptoms:
- muscle tension, which leads to their rapid tiredness, fatigue;
- pain, discomfort in the neck;
- A headache appears periodically.
Phase 2
The cracks of MPD, the exfoliates, the leaps even more, the protrusion is formed (protrusion of the fibrous membrane), bone growths occur along the edges of the vertebrae.
- A person has a creak, headache, sensitivity disorders, neck pain, which intensifies with elementary loads, gives other parts of the body.
- The sensations of pain in the neck have improved by loads, given behind, to the chest and the occipital part of the head.
- The person is regularly worried about serious headaches.
- Crystal when turning the neck.
- Difficulty in swallowing.
- Swanks of Blood Pressure.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness of the skin and fingers, weakening of the muscles of the limb.
Phase 3
In this phase, the protrusion breaks out (hernia), bone peaks increase in size, the ligaments of the spine are ossified in the attachment sites to the vertebral body. Symptoms for cervical osteochondosis in 3 phases:

- The symptoms of the first two phases of the disease are attached to a violation of the blood supply to the brain (due to the compression of the vertebral artery) in the form of visual imperfections, hearing, orientation, sensitivity and others.
- Pain can intensify with the most elementary movements (tilt your head), shoot the ear, jaw, shoulder and forearm.
- The patient is looking for a comfortable pose, trying to find an inclination of the head that relieves symptoms.
- His attention is dispersed, memory, vision, hearing, coordination of the movements are deteriorating, sleep disturbances appear, nausea, stable hypertension is formed.
- A pronounced rigidity of the spine, paresis, paralysis of the limbs (immobility, altered sensitivity), the muscles lose strength and the volume (atrophy) are united.
- The smooth curve of the spine is observed.
4th stadium
A characteristic of the fourth stadium: the symptoms of the osteocondrosis of the cervical column weaken, rigidity remains.
- The acute manifestations of the disease are mitigated due to the fact that soft tissues are subjected to ossification (OSSIFY).
- In 5 % of cases, 4 phases of osteochondrosis can be complicated by the necrosis of adjacent tissues, an ischemic stroke of the brain.
- The manifestations cause ischemic stroke (hunger for oxygen and drying part of the cells) and disabilities.
Possible complication of the cervical osteochondosis of the 4th degree:
- the ischemic stroke of the brain, which can lead to the patient's disability;
- Due to circulatory disorders of adjacent tissues, the patient may have trophic ulcers (cell death due to the lack of nutrients and oxygen).
Diagnostic methods
Osteocondrosis of the cervical region is diagnosed using various instrumental studies:
- X -Ray (characteristics of diagnostic characteristics in the form of peaks along the edge of the vertebra or a decrease in the height of the APD appear in 2 phases).
- CT, magnetic resonance imaging of the spine (allows you to diagnose changes in the APD in the initial phases).
- Discography (a study with the introduction of a contrast medium allows to establish the deepest damage to the intervertebral disc).
- Electronography (with its help determines the obstacle, inflammation during the nervous end).
- The dopplerography of the brain vessels (allows you to determine the condition of the blood vessels and the flow of blood in them).
In the event of damage to the nerve finals, numerous neurological manifestations of cervical osteochondrosis occur, it notes the symptoms and supervises the treatment of a neurologist (it helps to establish a diagnosis, recommends, prescribes drugs).
Treatment methods
Osteochondrosis of the neck is an incurable disease (such as osteochondosis of any other location), changes that occur in the tissues of the intervertebral disk, irreversible. In the early stages (1 and 2), conservative therapy can be suspended, in 3 phases the conservative treatment to relieve acute symptoms is prescribed. Sometimes with stable cervical root (with inflammation of the spinal nucleus of the spinal nerve), surgical removal of intervertebral discs is performed.
Emergency room
The emergency room for cervical osteochondosis is necessary if the patient feels acute pain in the neck, he cannot turn his head, he is unable to make other movements (raising his hands). In this case, a 2%solution of anesthetics or another drug with combined properties is introduced into the muscles along the vertebrae. The block quickly relieves pain and improves the patient's condition. The treatment of the osteocondrosis of the cervical column in the recovery period is carried out by heating agents that can improve blood circulation in the cervical vertebrae and on the mobility of the neck.
Other treatment methods:
Experts may recommend various orthopedic devices:
- Shaantsz's tire, which is a kind of corset, bandage or neck support. With its help, the head is fixed in a position and therefore relaxes the muscles, downloads and anesthetizes the cervical column.
- A orthopedic cushion that allows you to sleep in the cheaper and physiological installation for the cervical region, without causing muscle tension, pain and rigidity in the spine.
Surgery
Surgical treatment may be necessary if:
- The intervertebral hernia (or hernia) tightens the increasingly compressed nerve roots;
- Other methods of treatment do not relieve the patient's condition;
- There is a threat of disability.
Surgical treatment for cervical osteochondosis significantly improves the patient's conditions, but there is always the probability of developing various complications (loss of sensitivity, mobility of the spine).
Domestic treatment
The domestic treatment of osteocondrosis is the use of products that will help:
- Strengthen the blood circulation of the tissues.
- Improve the metabolism in them.
- Finally get rid of pain, inflammation and muscle tension.
Are used in the recovery period, when the acute symptoms of the disease are left behind:
- Renovation of heating with Alcohol Campaire. Take 50 ml of vodka, country alcohol, such as fresh aloe juice, 50 g of mustard powder and 100 ml of honey. Stir, add 3 egg proteins mounted to the mixture, leave for one day. By promptness, the mixture is applied to the affected area, along the ridge (for 2-3 hours), covered with plastic films on top. The course of treatment is 12 procedures, after a week it can be repeated.
- Ginger ointment. Grind 3 medium garlic and 50 g of fresh ginger root in a blender, add 50 g softened to the room temperature of the butter, beat again. With this tool, the damage area is smeared 1 time a day (for 2-3 hours), covered by a film at the top. The course of treatment for cervical osteochondrosis is 21 days, after a 2 -week break can be repeated.
Any non -traditional therapy methods should first be discussed with the attending physician.
Prevention
The measures for the prevention of osteocondrosis are:
- moderate physical activity and physical exercise for the neck;
- a diet rich in vitamins and useful for cartilage;
- orthopedic cushion and sleep mattress;
- Convenient workplace.
You must pay attention to the habit of transporting heaviness in a hand or a bag on one shoulder and get rid of it. A similar load is a provocative factor in the development of cervical osteocondrosis.
Forecast
Osteochondrosis is one of the most common pathologies which, after 45 years it appears in 90 % of people (regardless of gender). More often diagnosed:
- Cervical or cervical (due to the weakness of the cervical muscles and the mobility of the neck);
- lumbar osteochondrosis (due to the load on this vertebral column);
- Less commonly - thoracic (this department is less mobile, the load on it is small).
Violations due to which the disease appears is irreversible, therefore it is impossible to treat the pathology. Conservative methods can be suspended by the cervical osteochdrosis in phases 1 and 2. Raise the acute symptoms will need 2 to 3 weeks, until the complete restoration of the osteochondrosis is to be treated up to 6 months. At 3 and 4 phases, the most effective method is surgical correction (removal of hernias and discs, strengthening the vertebrae). A prerequisite for all people after 30 years is the regular performance of special exercises for the cervical column, because these measures solve the problem of the progression of the disease.























